Summary
Data center cooling is essential for maintaining optimal conditions for IT infrastructure, as the heat generated by servers can significantly impact overall energy consumption. Among the various cooling techniques employed, the introduction of Electronically Commutated (EC) fans has emerged as a game-changer in enhancing energy efficiency, revolutionizing the way data centers manage thermal loads. EC fans, which can reduce energy consumption by up to 80% compared to traditional AC fans, play a pivotal role in the transition towards sustainable data center operations, driven by both economic and ecological considerations.
The integration of EC fans into data center cooling systems reflects a broader trend towards automation and intelligent infrastructure management. Their ability to operate with variable speed control allows for real-time adjustments based on fluctuating cooling demands, making them particularly suited for the dynamic environments of modern data centers. This adaptability not only enhances cooling efficiency but also aligns with regulatory initiatives, such as the European Union’s Energy Efficiency Directive, which emphasizes the need for improved energy consumption metrics in data centers.
However, the adoption of EC fans is not without challenges. Initial investment costs, technical complexity in system integration, and the necessity for ongoing regulatory compliance pose hurdles for operators. Additionally, while the long-term energy savings can offset these costs, the upfront expenditure may deter some organizations from transitioning to this advanced technology. Despite these obstacles, the growing emphasis on sustainability in the industry, coupled with advancements in smart technologies, indicates that EC fans will likely play an increasingly crucial role in the future of data center cooling solutions.
Overall, the rise of EC fans represents a significant shift in data center operations, positioning them as vital components in the quest for greater energy efficiency and reduced environmental impact. As businesses prioritize sustainable practices and navigate evolving regulatory landscapes, the integration of EC fans technology will be instrumental in optimizing cooling systems and meeting both operational and environmental objectives.
Table of Contents
Data Center Cooling Techniques
Data center cooling is critical for maintaining optimal operating conditions for IT equipment. Various techniques have been developed to efficiently manage heat generated by servers, which can account for a significant portion of a data center’s overall energy consumption.
Types of Cooling Systems
Data center cooling solutions generally fall into three main categories: air-based systems, liquid-based systems, and hybrid systems.
Air Cooling Systems
Air cooling systems are the most prevalent method used in data centers, accounting for over 80% of cooling implementations. These systems typically employ air handling units, cooling coils, and fans to regulate temperature and airflow. In traditional setups, cooled air is distributed either through raised floors or suspended ceilings, moving upward toward server racks. As the air circulates around the servers, it absorbs heat, which is then expelled as hot air.
Advanced air cooling techniques include:
- Raised Floor Cooling: This system utilizes a plenum under raised floors to distribute cooled air directly to server inlets.
- In-Row Cooling: Units placed between server racks provide targeted cooling to high-density areas.
- Aisle Containment: Physical barriers separate cold and hot aisles, preventing air mixing and improving cooling efficiency.
Liquid Cooling Systems
Liquid cooling systems offer a more efficient alternative, especially for high-density environments. These systems use liquid coolants to absorb and transport heat away from server components, often resulting in superior thermal management.
- Direct-to-Chip Cooling: A heat exchanger is directly attached to CPUs or other heat-generating components, allowing liquid to absorb heat before being cooled and recirculated.
- Immersion Cooling: Servers are submerged in a dielectric fluid that absorbs heat directly, subsequently passing through a heat exchanger for cooling.
Although initially more expensive and complex to maintain compared to air cooling systems, liquid cooling can lead to lower long-term energy costs and minimized thermal downtime.
Evaporative Cooling Systems
Evaporative cooling is an emerging technique that leverages the cooling effect produced when water evaporates. In this method, fans push warm air over chilled water or coolant pads, resulting in a temperature drop. This approach can be particularly cost-effective and energy-efficient, especially in low-humidity environments, with a reported water usage effectiveness (WUE) of 1.8 liters per kWh. However, implementing evaporative cooling can pose challenges, particularly in areas with high humidity where the system may be less effective.
Design Considerations
When designing a cooling system for a data center, several critical factors must be considered.
- Capacity Planning: The cooling system must be able to manage the heat load generated by IT equipment, which varies based on equipment type and density.
- Redundancy: To ensure continuous operation, cooling systems should incorporate backup components, such as redundant chillers and pumps.
- Air and Water Flow Paths: Effective design includes multiple pathways for air and water, enhancing reliability and performance during potential blockages.

EC Fans
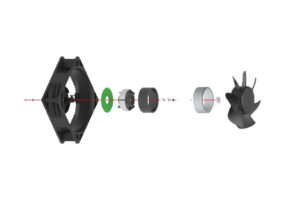
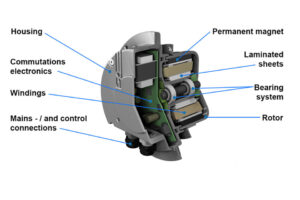
Electronically commutated (EC) fans have emerged as a critical component in enhancing energy efficiency across various applications, including data centers, refrigeration systems, and HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) units. These fans are gaining popularity due to their remarkable energy efficiency, capable of reducing energy consumption by up to 80% compared to traditional AC fans. This efficiency not only translates to significant operational cost savings but also contributes to a reduced environmental impact, aligning with the growing focus on sustainability in building design and operation.
Benefits of EC Fans
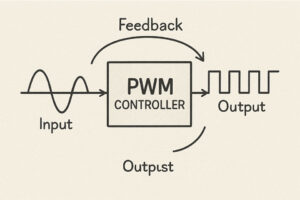
The primary advantage of EC fans lies in their ability to operate with variable speed control, which allows for real-time adjustments based on demand. This adaptability is particularly beneficial in environments like data centers, where cooling requirements can fluctuate dramatically. The lifespan of EC fans ranges from 30,000 to 70,000 hours, further underscoring their cost-effectiveness and lower maintenance needs compared to conventional fan systems.
Additionally, the integration of EC fans into cooling systems supports energy conservation efforts. As organizations increasingly adopt smart building technologies, the demand for efficient cooling solutions like EC fans is expected to rise, driven by the pursuit of both economic and ecological benefits. With the implementation of IoT and predictive maintenance technologies on the horizon, the functionality and efficiency of EC fans are poised for further enhancement, making them an essential consideration for businesses aiming to optimize their operations in a sustainable manner.
Role in Data Centers
Data centers are notorious for their high energy consumption, accounting for approximately 2.7% of electricity usage in Europe, a figure projected to rise to 3.21% by 2030. As a response, many data center operators are increasingly adopting energy efficiency tools and strategies, including the integration of EC fans. The European Union’s Energy Efficiency Directive (EED) has also highlighted the need for improved energy consumption metrics in data centers, emphasizing the role of efficient cooling solutions like EC fans in achieving regulatory compliance.
Moreover, the rise of smart data center management systems, such as Daikin’s Intelligent Data Centre Manager, exemplifies how EC fans can be utilized to optimize operations. These systems leverage artificial intelligence to monitor and adjust cooling infrastructure dynamically, enhancing overall performance and energy savings. As businesses seek to balance operational efficiency with environmental responsibility, the deployment of EC fans in data centers represents a significant step toward sustainable energy management.
Impact of EC Fans on Energy Efficiency
EC fans, or electronically commutated fans, are increasingly recognized for their significant contributions to energy efficiency, particularly in data centers and other energy-intensive applications. One of the primary advantages of EC fans is their energy efficiency, which can reduce energy consumption by up to 80% compared to conventional AC fans. This substantial reduction in energy use not only leads to lower operational costs but also supports broader environmental sustainability efforts.
Adoption in Data Centers
The integration of EC fans technology in data centers is part of a larger trend towards intelligent, adaptive infrastructure. As facilities evolve into more automated and data-driven environments, components like EC axial fans become essential due to their ability to interface with building management systems and respond to real-time analytics. This shift is not limited to new constructions; many operators are retrofitting existing systems with EC fans to capture energy savings and extend the life of their infrastructure. The plug-and-play nature of EC fan designs allows for straightforward upgrades without requiring significant system overhauls.
Energy Consumption and Cost Savings
EC fans demonstrate remarkable efficiency, operating at levels as high as 90%, which is significantly greater than traditional AC fans. This high efficiency translates into direct energy savings, with EC fans consuming up to 70% less energy than their AC counterparts. The U.S. Department of Energy highlights the critical role of electric motor-driven systems in overall energy consumption, noting that around 25% of energy in residential and commercial sectors is used by these systems. By replacing less efficient fans with EC fans, businesses can achieve substantial reductions in energy usage and associated costs.
Design and Operational Benefits
In addition to energy savings, EC fans offer design flexibility, as they can serve as drop-in replacements for AC fans while maintaining the same interface. This feature is particularly beneficial in retrofitting scenarios, where upgrading to more efficient technologies is essential for meeting stringent energy efficiency standards. Furthermore, EC fans are capable of driving both axial and radial fans, making them versatile for various applications. The elimination of sparking and electromagnetic interference in EC motors enhances their reliability, reducing maintenance requirements and long-term operational costs.
Future Trends
Looking ahead, the market for EC fans is projected to grow steadily, driven by the increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions across multiple industries. As technologies such as artificial intelligence and machine learning advance, their applications in data center cooling will likely become more sophisticated, leading to even greater efficiencies and sustainability in thermal management practices. Overall, the impact of EC fans on energy efficiency represents a pivotal advancement in addressing the power and energy challenges faced by modern data centers.

Challenges and Considerations
The transition from traditional fan systems to Electronically Commutated (EC) fans in data centers presents several challenges and considerations that must be addressed for successful implementation.
Regulatory Landscape
The evolving regulatory frameworks, particularly in the U.S. and Europe, are pushing the adoption of energy-efficient systems. In the U.S., the EPA has tightened energy performance standards through its Energy Star and Green Building certification schemes, promoting energy-optimized solutions in the industry. Similarly, the EU’s Ecodesign Directive sets minimum efficiency thresholds for motors and fans used in HVAC systems, creating a compliance-driven market for EC technologies. This shift necessitates that data center operators not only adopt new technologies but also keep abreast of regulatory changes and ensure compliance to avoid penalties.
Technical Complexity
Data centers are characterized by their technical complexity, which can pose challenges in integrating new cooling technologies. The need for precise airflow and temperature control often requires a thorough understanding of existing systems and their interactions. While EC fans offer enhanced performance and efficiency, facilities managers must assess the specific needs of their data centers, including sustainability goals and overall operational costs, to ensure that the chosen solution is optimal for their environment.
Cost and Investment Recovery
Although EC fans lead to significant energy savings, the initial investment can be a hurdle for some organizations. Many businesses recover their investment within five years due to the ongoing energy savings these fans provide. However, this recovery period might still be perceived as a barrier, especially for smaller enterprises with limited budgets. Thus, cost-benefit analyses become essential for decision-makers to justify the transition to EC technology.
User-Friendliness and Integration
Another consideration is the user-friendliness of EC fans compared to traditional systems. While EC fans simplify many operational aspects—such as eliminating the need for belts and pulleys—they also require facilities managers to adapt to new maintenance protocols and monitoring technologies. The ease of integrating these systems into existing frameworks is crucial, as reliable performance and remote maintenance capabilities enhance their attractiveness to operators.
Environmental Impact
Finally, the environmental impact of cooling systems cannot be overlooked. Decisions made in data center operations have far-reaching consequences on energy consumption and carbon footprints. Striking a balance between digital demands and sustainability efforts is essential, and data center operators are increasingly held accountable for their environmental impact under various regulatory frameworks. Thus, understanding the holistic effects of cooling solutions—both in terms of efficiency and environmental sustainability—is paramount for long-term success in the industry.
Industry Influence
Role of Authorized Dealers and Distribution Networks
In the offline distribution channel, authorized dealers and distributors play a crucial role in the supply chain of electronically commutated (EC) fans. These intermediaries have established relationships with end-users and offer value-added services such as installation, maintenance, and aftersales support. Their trustworthiness and reliability make them a preferred choice for customers, especially in the commercial and industrial sectors, where the presence of robust distribution networks ensures that EC fans are readily available across various regions, driving market growth.
Strategic Collaborations and Market Trends
Key players in the EC fan market frequently employ strategic collaborations, mergers, and acquisitions to enhance their market presence and gain a competitive edge. By partnering with technology providers, manufacturers can integrate advanced features into their EC fans, including IoT-enabled controls and smart sensors. These collaborations facilitate the sharing of expertise and resources, leading to the development of innovative products that meet the evolving demands of consumers.
Furthermore, compliance with evolving regulatory requirements unlocks incentives and rebates offered by federal and state programs, effectively reducing the total cost of ownership for end-users. The need for close collaboration with standards agencies and continuous performance testing is vital for manufacturers to navigate regulatory shifts and maintain their market position. The burgeoning green building sector is forecasted to account for over 50% of new U.S. commercial construction by 2030, presenting significant opportunities for EC fans that meet energy efficiency standards.
Impact of Sustainability Trends
The push toward sustainability significantly influences the data center industry, with many companies now prioritizing eco-friendly practices. An estimated 62% of businesses have implemented sustainability strategies, with a notable 68% transitioning to more sustainable materials and lower-emission alternatives. This trend is reflected in the adoption of energy-efficient cooling solutions, such as EC fans, which support the industry’s commitment to minimizing environmental impact.
Additionally, regulatory frameworks like California’s Title 24 Building Energy Efficiency Standards mandate the adoption of smart, energy-efficient HVAC components, thus accelerating the market penetration of EC fans. The emphasis on energy efficiency and sustainability in data centers creates a favorable environment for product differentiation based on eco-friendly credentials and smart features, enabling manufacturers to capitalize on lucrative retrofit markets and build long-term customer relationships.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite the opportunities, companies must remain vigilant about regulatory compliance and evolving market dynamics. Data center operators face challenges in adapting to new regulations regarding energy efficiency and sustainability, particularly as governments worldwide implement stricter standards. Effective management and strategic positioning around technological innovations are essential for manufacturers to maintain competitive advantages and align their product portfolios with the global transition toward sustainable infrastructure.

Future Trends in Data Center Cooling
The future of data center cooling is marked by innovative technologies and regulatory shifts aimed at enhancing energy efficiency and sustainability. As the demand for data centers continues to surge, it is essential to adopt cooling solutions that not only meet the performance needs but also minimize energy consumption and environmental impact.
Advancements in Cooling Technologies
Emerging technologies such as immersion cooling and magnetic refrigeration are set to transform the landscape of data center cooling. Immersion cooling involves submerging electronic components in a thermally conductive liquid, which can significantly lower energy usage and improve cooling efficiency compared to traditional air cooling systems. Similarly, magnetic refrigeration, which utilizes magnetocaloric effects, offers an energy-efficient alternative that has the potential to reduce power consumption considerably while maintaining optimal operating conditions.
EC Fans and Energy Efficiency
Electronically commutated (EC) fans are increasingly recognized for their ability to improve energy efficiency in data centers. Unlike traditional induction motors, EC fans use brushless DC motors that allow for precise control of fan speed and airflow, resulting in energy savings of up to 70% in some applications. Their capability to adjust output in real time based on temperature and airflow requirements makes them particularly suitable for cooling specific areas within data centers, thus reducing overall power consumption. The integration of variable speed drives and high-end control systems further enhances the efficiency of these cooling solutions.
Regulatory Impact and Sustainability
As governments worldwide implement stricter regulations on energy consumption and greenhouse gas emissions, data center operators are compelled to adapt their cooling systems to meet new standards. The European Union’s revised Energy Efficiency Directive mandates data center owners to report energy and water usage annually, pushing for a target power usage effectiveness (PUE) of 1.3 or lower by 2025. In the United States, similar climate disclosure laws are being introduced, emphasizing the importance of sustainability in operational practices. These regulatory measures not only encourage the adoption of energy-efficient technologies but also unlock incentives that can significantly lower operational costs for data center operators.
Capacity Planning and Redundancy
Looking ahead, effective capacity planning and redundancy in cooling systems will be critical considerations for data center design. As the heat generated by IT equipment increases, cooling systems must be scalable to accommodate growth and expansion without compromising performance. Moreover, incorporating redundant components—such as chillers and cooling towers—ensures uninterrupted operation even in the event of a system failure, which is vital for maintaining reliability in data center environments.