Summary
The distinction between Direct Current (DC) fans and Electronically Commutated (EC) fans lies in their operational principles, efficiency, and applications. DC fans are powered by a stable voltage source and are commonly used in environments where low noise and energy efficiency are paramount. They are versatile components found in various sectors, including household appliances, telecommunications, and medical equipment, prized for their adjustable speed control and reliability. However, they often require a higher initial investment and may be limited in their control features compared to AC fans.
In contrast, EC fans leverage both AC and DC voltages, integrating advanced electronic controls that allow for precise modulation of airflow and energy consumption. This technology significantly enhances their efficiency, making EC fans particularly suitable for complex systems like HVAC installations, where dynamic airflow management is crucial. Their brushless design reduces mechanical wear and increases longevity, yet they can also be cost-prohibitive for some users due to their sophisticated technology.
The growing market for both fan types reflects an increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions across industries, driven by advancements in technology and heightened environmental consciousness. DC fans are expected to see substantial growth, projected to reach USD 3.2 billion by 2033, as sectors like healthcare and electronics continue to prioritize effective thermal management. Meanwhile, EC fans are favored for their ability to comply with stringent energy regulations, reducing operational costs and carbon emissions.
While both fan types offer distinct advantages, their selection often hinges on specific application requirements, including efficiency, cost, and control capabilities. The on-going debate regarding their environmental impact highlights the need for sustainable manufacturing practices, as both types face challenges related to material use and energy consumption. As innovations in fan technology continue to evolve, both DC and EC fans are positioned to play integral roles in enhancing energy performance in diverse settings.
Table of Contents
Technical Differences
Power Supply and Operation
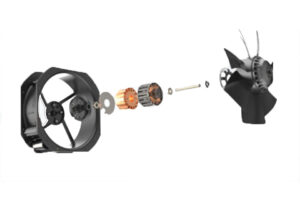
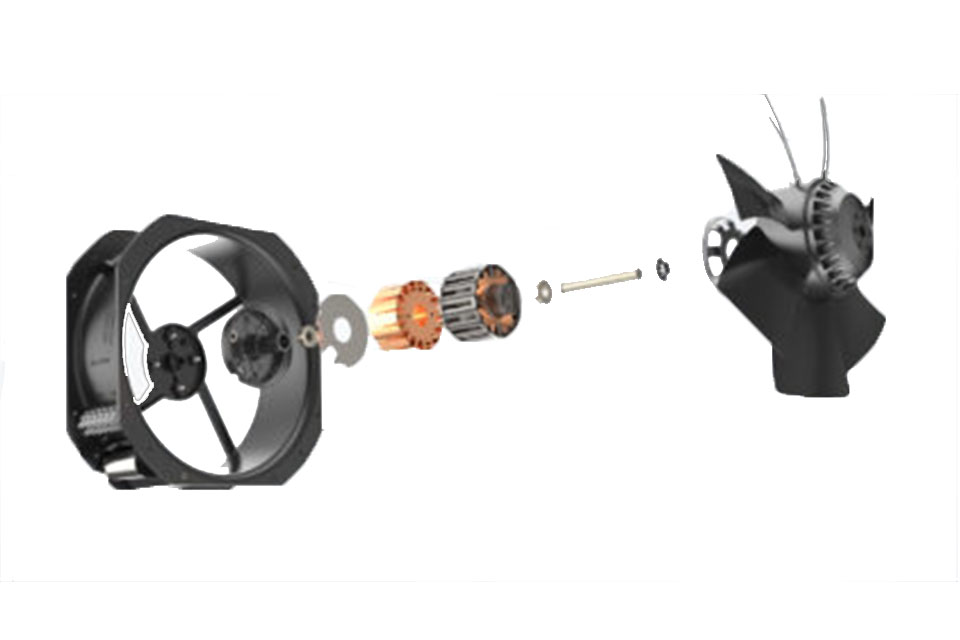
DC fans, or direct current fans, operate using a stable and constant voltage source, typically ranging from 3V to 48V, supplied by batteries or DC power supplies. In contrast, Electronically Commutated (EC) fans function by utilizing both AC and DC voltages, which allows them to harness the advantages of both power types. The EC motor incorporates internal voltage transformation to enable operation on a single-phase or three-phase AC supply, such as 230VAC or 400VAC, while still utilizing a DC voltage for its operation.
Efficiency and Control
EC technology is known for its very high degree of efficiency, significantly surpassing traditional DC fan technologies. This is largely attributed to the integrated controller in EC fans, which provides continuous control over operations like airflow, pressure, and speed adjustments. DC fans, while generally more efficient than AC fans, lack the advanced control features found in EC fans, making them less versatile in applications requiring precise adjustments.
Design and Construction
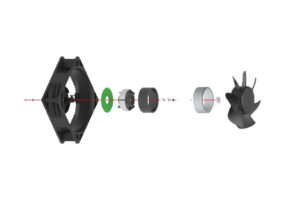
The working principle of DC fans involves the interaction of electric current with a magnetic field generated by the coils wound around the impeller shaft, which facilitates rotational movement. EC fans, on the other hand, utilize a brushless design that reduces mechanical wear and increases reliability over time. The EC motor design incorporates an electronic circuit board that not only transforms AC to DC but also manages the commutation process, leading to improved performance and longevity.
Thermal Management
When comparing thermal performance, it is essential to consider that DC fans can lose approximately 20% of energy as heat during operation, which can affect overall efficiency. EC fans, with their advanced controls and design, typically operate at lower temperatures, mitigating energy loss and enhancing system reliability.
Application Suitability
DC fans are widely used in applications where low noise and efficiency are prioritized, while EC fans are preferred in more complex systems requiring dynamic control of airflow and efficiency, such as in HVAC systems or high-performance cooling applications. The selection between these two types of fans ultimately depends on the specific requirements of the application, including efficiency, control precision, and thermal management needs.

Applications
DC fans and EC fans are employed in a wide array of applications across various industries, capitalizing on their energy efficiency and performance characteristics.
General Applications
DC fans are known for their versatility and are used in numerous sectors, including household appliances, renewable energy systems, and aerospace. For instance, they enhance air circulation in refrigerators and air purifiers, while also facilitating cooling in solar inverters and wind turbines. Their ability to operate quietly makes them particularly suitable for noise-sensitive environments such as bedrooms and home offices, where maintaining a tranquil atmosphere is essential.
Industrial and Commercial Uses
In industrial applications, DC fans play a crucial role in thermal management. They are often integrated into telecommunications, server, and data storage systems, where efficient airflow is vital for maintaining optimal operating temperatures. These fans can be equipped with advanced features like tachometer feedback and variable voltage options, which enhance system diagnostics and integration. The industrial sector has seen a significant demand for these devices, accounting for over 42% of the market share in 2023.
Medical and Sensitive Environments
DC fans are particularly valued in medical settings due to their low noise operation and reliability. They are frequently utilized in ventilators and patient monitors, ensuring that essential medical equipment operates quietly without compromising performance. This reliability and energy efficiency make them indispensable in applications where both performance and a quiet environment are critical.
Environmental Considerations
Both DC and EC fans contribute to energy efficiency, aligning with modern environmental responsibilities. They are designed to consume less power than traditional AC fans, thereby reducing carbon emissions and energy costs. This advantage makes them a sustainable choice for companies looking to enhance their energy performance while minimizing their ecological footprint.
Future Prospects
As the demand for energy-efficient solutions continues to grow, the applications for DC and EC fans are expected to expand. Innovations in technology will likely enhance their performance capabilities, further embedding them in both existing and emerging markets. With ongoing investments in R&D, companies like INFINAIR and others are poised to lead advancements in fan technology, tailoring solutions to meet diverse industry needs.

Advantages and Disadvantages
DC fans and EC (Electronically Commutated) fans offer distinct benefits and drawbacks that influence their selection for various applications.
Advantages of DC Fans
One of the most significant advantages of DC fans is their high efficiency, consuming significantly less power than traditional AC fans, often up to 50% less electricity. This energy efficiency translates into lower operational costs, making DC fans a cost-effective choice in the long term, despite their higher initial purchase price, which typically exceeds $200. Furthermore, DC fans provide adjustable speed control, enhancing their versatility for different applications, from residential environments to industrial settings.
DC fans are also renowned for their low noise operation. Their design, which often includes advanced blade technology and superior bearings, can result in noise reductions of up to 10 dB compared to standard models, making them particularly suitable for sensitive environments like home theaters and medical facilities. Additionally, these fans exhibit impressive durability and reliability, engineered to withstand harsh operating conditions, which further extends their lifespan. Their lightweight design facilitates installation and integration into various systems.
Advantages of EC Fans
EC fans similarly boast high efficiency and are particularly advantageous due to their integrated controller, allowing for continuous control and additional functionality. This integration simplifies connections and enhances system performance. Like DC fans, EC fans are also designed for energy efficiency, making them ideal for environments where reducing energy consumption is critical. They are particularly favored in applications requiring constant airflow, such as HVAC systems, where their efficiency can lead to significant cost savings over time.
Disadvantages of DC Fans
Despite their advantages, DC fans come with some drawbacks. The most prominent is their higher cost compared to AC fans, which can make initial adoption more challenging for budget-conscious consumers. Additionally, most DC fans typically come equipped with remote controllers that may not be as functional or reliable as traditional wall-mounted controls, raising concerns about user convenience.
Disadvantages of EC Fans
EC fans can also be more expensive than their AC counterparts due to their advanced technology and integrated controls. While they offer substantial energy savings, the initial investment may not be easily justifiable for all users, especially in applications with lower demand for energy efficiency. Furthermore, the complexity of their systems might necessitate specialized knowledge for installation and maintenance, potentially deterring some users.
Market Trends
The market for DC fans is experiencing significant growth, with projections indicating it will reach USD 3.2 billion by 2033. This growth is anticipated to follow a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.39% from 2025 to 2032. The increasing demand for energy-efficient cooling solutions across various sectors, particularly in electronics and healthcare, is a primary driver of this trend. In the healthcare industry, the adoption of temperature control systems in medical devices is expected to contribute to substantial growth in the use of DC fans, reflecting the rising need for reliable thermal management in critical applications.
In the industrial sector, DC air movers accounted for over 42% of the market share in 2023, highlighting their significance in enhancing operational efficiency. The versatility and efficacy of blower DC devices across multiple applications have positioned them as essential components in modern electronic systems, particularly in regions experiencing rapid industrial growth, such as Asia Pacific. These trends are further supported by government incentives aimed at promoting energy-efficient appliances, which have increased consumer interest and demand for DC technology.
Additionally, the competitive landscape is marked by key players such as Delta Electronics, Nidec Corporation, and Sanyo Denki, who are actively engaged in product innovation and strategic partnerships to meet the evolving demands of end-users. As industries continue to recognize the importance of effective thermal management, the adoption of blower DC fans is expected to rise, underlining their critical role in improving product reliability and performance. The durability and energy efficiency of these fans, which can save up to 70% less power than traditional AC fans, further enhance their appeal in both residential and commercial markets.
Environmental Impact
The environmental impact of DC (Direct Current) fans and EC (Electronically Commutated) fans is an important consideration for manufacturers and consumers alike, especially as awareness of sustainability grows.
DC Fans and Their Environmental Footprint
DC fans are recognized for their reliability and robust construction, enabling them to perform in various industrial settings, even under harsh conditions such as extreme temperatures and moisture. However, the materials used in their construction often derive from non-renewable resources, primarily plastics and metals that can contribute to environmental degradation during production and disposal. Traditional plastics used in fan blades can take hundreds of years to decompose, creating significant waste in landfills. Despite their durability, the long-term environmental implications of using non-eco-friendly materials remain a challenge.
Efforts to incorporate recyclable and eco-friendly materials, such as aluminum and bamboo-based composites, have emerged in the design of DC fans. Aluminum is favored for its recyclability, while bamboo offers a sustainable alternative that can potentially reduce the overall carbon footprint associated with fan production.
EC Fans: A Sustainable Alternative
In contrast, EC fans are designed with advanced features that not only improve energy efficiency but also promote environmental sustainability. By consuming up to 50% less electricity than traditional AC motors, EC fans significantly lower operational costs and reduce carbon emissions, making them a more environmentally responsible choice. Their construction often incorporates materials that are less harmful to the environment and more recyclable, contributing to a reduced overall ecological footprint.
Furthermore, EC fans are increasingly being adopted in various industries to comply with stringent energy efficiency regulations in the U.S. and Europe, helping to minimize energy consumption and emissions at scale. The integration of synchronous reluctance motors in EC fan technology also reduces reliance on rare earth materials, promoting a more sustainable manufacturing process.