Summary
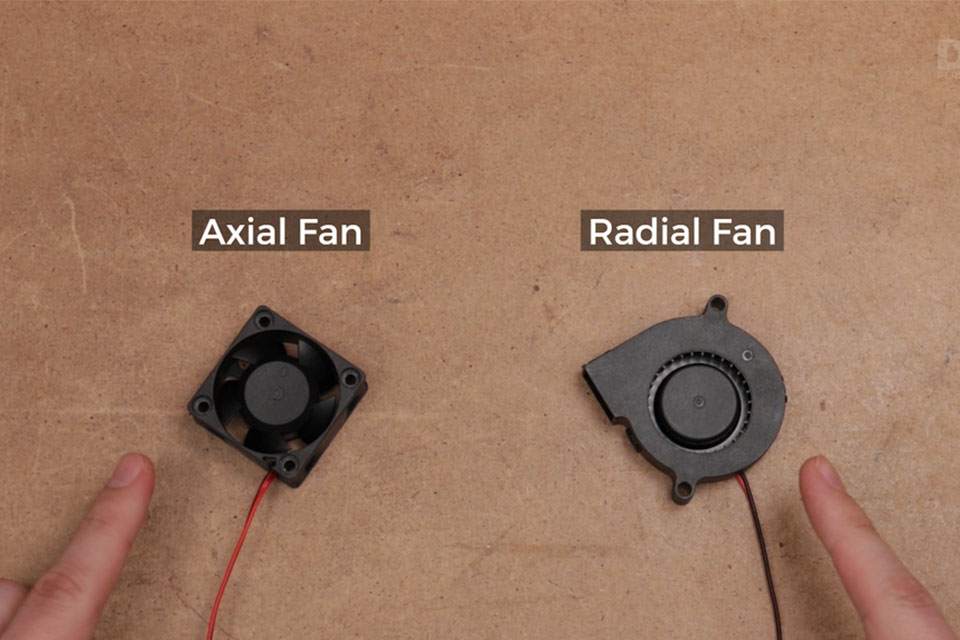
Radial fans, also known as centrifugal fans, are essential mechanical devices that use centrifugal force to move air or gases, playing a critical role in various industrial and commercial applications, including HVAC systems, ventilation, and material handling. Their design, which has evolved significantly since the 19th century, emphasizes efficiency and performance, making them a staple in industries that require effective airflow management under high resistance conditions. The growing emphasis on energy efficiency and environmental sustainability has further elevated the importance of radial fans in modern engineering practices, with efficiency levels reaching up to 92% in recent innovations.
The notable advancements in radial fan technology stem from the integration of improved materials, motor types, and design methodologies. The transition from mechanical designs to the incorporation of electric motors during the industrial revolution marked a turning point, enabling more powerful and efficient fan systems suitable for diverse applications. More recently, electronically commutated (EC) motors and variable frequency drives (VFDs) have revolutionized performance, allowing for enhanced speed control and significant reductions in energy consumption compared to traditional AC motors.
Despite their widespread use and advancements, radial fans are not without controversy. Issues related to energy consumption and operational noise levels have sparked debates about their environmental impact, particularly in sensitive applications. Manufacturers are increasingly focusing on compliance with energy efficiency standards and noise regulations, striving to balance performance with ecological responsibility. Furthermore, concerns regarding indoor air quality in industrial settings emphasize the necessity for effective ventilation solutions, highlighting the dual role of radial fans in promoting both productivity and worker safety.
In summary, radial fans serve as a vital component in numerous sectors, reflecting a blend of historical development and modern technological innovations. Their significance continues to grow as industries face increasing pressure to adopt energy-efficient and environmentally friendly practices, making them a focal point in discussions about industrial sustainability and performance optimization.
Table of Contents
History
Radial fans, also known as centrifugal fans, have a long-standing history rooted in the development of fan technology that dates back several centuries. Their design, which utilizes centrifugal force to move air or gases, has evolved significantly over time, leading to advancements in efficiency and performance.
Early Developments
The fundamental principles of fan operation have been understood for hundreds of years, but the specific design of radial fans began to take shape in the 19th century. Early designs were primarily mechanical and lacked the efficiency that modern technology affords. However, these initial models laid the groundwork for further innovation, emphasizing the importance of airflow dynamics and pressure generation, which are critical for various applications in industrial settings.
Technological Advancements
As the industrial revolution progressed, so too did the science of fan design. By the mid-20th century, advancements in materials and motor technology allowed for the creation of more efficient and powerful radial fans. Notably, the introduction of electric motors significantly improved the performance of fans, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, from HVAC systems to material handling in factories.
Recent Innovations
In recent decades, there has been a notable focus on energy efficiency in fan design. Organizations and manufacturers have prioritized the development of fans that not only meet performance standards but also comply with strict energy efficiency classifications.
Modern radial fans can achieve efficiency levels of up to 92%. The integration of electronically commutated (EC) motors has revolutionized the industry, allowing for stepless speed control and substantial reductions in energy consumption compared to traditional AC motors.
Manufacturers like EBM-Papst have led the way in setting industry standards for energy-saving technologies, which has influenced fan design globally, particularly in markets like Europe, North America, and China. This evolution reflects the increasing demand for environmentally friendly and economically viable industrial solutions.
Design and Construction
Factors Influencing Design
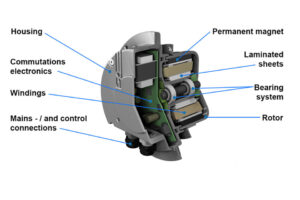
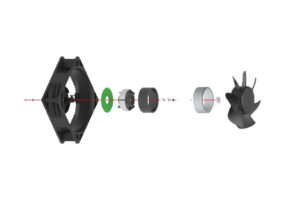
The design of radial fans is fundamentally shaped by several key factors, including aerodynamic design, motor type, materials selection, and operational conditions. These elements collectively influence the fan’s efficiency, airflow rate, and pressure characteristics. A thorough understanding of the operational principles and performance ratings is essential for engineers to select the appropriate type of radial fan tailored to specific industrial applications.
Blade Material and Configuration
The choice of blade material is critical in determining a fan’s overall performance, strength, and noise levels. Lightweight materials like aluminum and composites are advantageous for energy efficiency, but they may compromise structural integrity.
In contrast, heavier materials like steel enhance durability, making them suitable for industrial applications, albeit with higher energy consumption. Additionally, plastics are often selected for their economic benefits and corrosion resistance, though they exhibit limitations at elevated temperatures.
Blade Pitch and Design
Blade design significantly impacts airflow efficiency and energy consumption. Factors such as blade shape, pitch angle, and rotation speed contribute to the fan’s capability to move air effectively. Larger blades with higher pitch angles generally provide improved airflow efficiency. Furthermore, the quality of the motor plays a pivotal role, as higher-powered motors can enhance performance by reducing drag and noise, thereby improving overall airflow.
Efficiency Considerations
To optimize efficiency, it is essential to evaluate airflow requirements, noise levels, and budget constraints. By conducting a meticulous assessment of these factors, engineers can make informed decisions that align with the cooling needs of their projects.
For instance, an appropriate fan design that matches the room area and intended activity can maximize productivity and comfort while minimizing energy waste.
Innovations in Design
Recent advancements in design optimization techniques, such as genetic algorithms, have facilitated the development of innovative housing designs for radial fans. These improvements enable engineers to create more efficient blower systems that better meet the demands of variable speed drives in various applications. Additionally, partnerships with specialized manufacturers can help tailor solutions to specific needs, ensuring high reliability and performance in critical systems.
Operating Principles
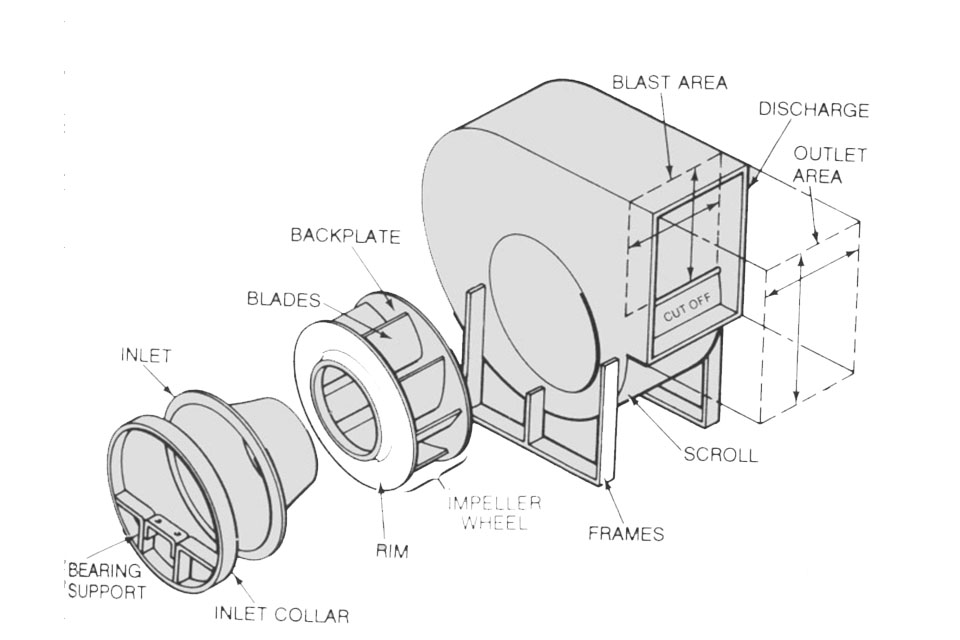
Radial fans, also known as centrifugal fans, operate on the principle of centrifugal force, which enables them to expel air at a right angle to the axis of the impeller. As the impeller rotates, it draws air into its center, where it gains kinetic energy before being discharged through the volute or scroll housing. This design facilitates a significant increase in static pressure, making radial fans particularly effective in applications that encounter high resistance, such as ducted systems or exhaust configurations.
Fan Design and Efficiency
The efficiency of radial fans is influenced by several factors, including the design of the impeller, the type of motor used, and the operational conditions under which the fan operates. Evaluating performance ratings helps engineers choose devices that optimize energy consumption while fulfilling operational requirements. Additionally, the airflow requirements of a specific application dictate the size and configuration of the fan, as well as the necessary static pressure the system must maintain.
Applications and Performance
Centrifugal fans are widely employed in various industrial applications, ranging from HVAC systems to pneumatic conveying systems, where they effectively manage airflow in challenging environments. Their ability to maintain consistent airflow is critical for processes that involve the transport of materials like grains and powders. The increasing demand for robust performance in industrial processes has contributed to the growing preference for centrifugal blowers, despite their higher energy consumption compared to axial fans.
The long-term performance and durability of radial fans are often quantified using the L10 life rating, which predicts the operational lifespan of a fan based on statistical forecasts. This rating is significantly influenced by factors such as bearing type and operating temperature, with ball bearings generally offering a longer lifespan than sleeve bearings under high-temperature conditions. Thus, manufacturers prioritize the selection of high-quality materials and engineering practices to enhance fan reliability and efficiency.
Applications
Radial fans, also known as centrifugal fans, play a pivotal role across various industries due to their efficiency in moving air and creating pressure. Their diverse applications can be categorized into several key sectors.
HVAC Systems
Radial fans are extensively utilized in Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems. They are crucial for circulating air, maintaining temperature control, and ensuring adequate ventilation in both commercial and industrial settings. By generating high static pressure, these fans can efficiently move air through ducts and other system components, which is essential for effective climate control.
Industrial Ventilation
In industrial environments, radial fans are integral to ventilation systems. They help remove contaminants, control humidity, and ensure a safe working atmosphere by swiftly moving large volumes of air. This is particularly important in settings like factories and warehouses, where air quality directly impacts worker safety and productivity.
Cooling Applications
Radial fans are vital in cooling applications, especially in manufacturing processes that generate excess heat. They assist in dissipating heat to prevent equipment overheating, thus maintaining optimal operating conditions for machinery and electronic components. For instance, they are employed in cooling systems for industrial machinery and electronic temperature management, where heat dissipation is critical.
Drying Processes
The efficiency of radial fans extends to drying applications. They facilitate rapid drying of agricultural products and curing processes in manufacturing by circulating air and removing moisture from surfaces. This capability is essential in various industries where moisture control is crucial for product quality and longevity.
Material Handling
Radial fans are also utilized in material handling systems, particularly in pneumatic conveying applications. They help transport materials by creating the necessary airflow to move bulk products, making them essential in industries such as food processing and pharmaceuticals.
Specialty Applications
Additionally, radial fans find uses in specialty applications, such as dust control in construction sites and the food industry, where tailored solutions are necessary to meet specific operational requirements. Case studies have shown that the effective use of radial fans in these settings leads to improved air quality and reduced maintenance needs.
Efficiency and Performance
Centrifugal fans, particularly those with radial blades, exhibit varying efficiency levels influenced by several design and operational factors. The motor type, blade geometry, and housing configuration all contribute significantly to overall performance. Two primary motor types are commonly used in centrifugal fans: asynchronous (AC) motors, which are widely utilized for their simplicity and constant speed, and electronically commutated (EC) motors, which offer energy efficiency and better integration with building automation systems.
Blade Design and Performance
Blade design is a crucial factor that impacts the efficiency of centrifugal fans. The curvature and geometry of the blades play a significant role in determining airflow and pressure generation.
Backward curved blades are designed to minimize turbulence and provide efficient airflow patterns, making them ideal for applications requiring higher static pressures. In contrast, forward curved blades, while generating higher airflow rates, can lead to increased turbulence and reduced efficiency in high-pressure scenarios.
Radial blades are robust and capable of handling high resistance, making them suitable for industrial environments but potentially noisier and less efficient compared to their backward curved counterparts.
Performance Ratings
Evaluating the performance ratings of centrifugal fans is essential for optimizing energy consumption and reducing operational costs. Factors such as design, motor type, and specific operational conditions can significantly influence fan efficiency. The ‘wire to air’ efficiency, which takes into account both electrical and mechanical performance, is a vital metric for assessing overall efficiency. For example, the calculation of fan efficiency involves considering the Volume Flow and Fan Total Pressure, allowing engineers to determine the effective performance of a fan in relation to its absorbed power.
Impact on Air Quality
The importance of efficient airflow is underscored by studies indicating that indoor air can be significantly more polluted than outdoor air, highlighting the necessity of selecting devices that enhance air quality while maintaining energy efficiency. As energy efficiency remains a top priority for HVAC system designers and operators, advances in fan technology, particularly with the integration of EC motors and optimized blade designs, are vital for meeting the growing demand for effective air movement solutions in various industrial applications.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Routine maintenance and effective troubleshooting are crucial for ensuring the longevity and performance of radial fans. Regular inspections and timely interventions can prevent minor issues from escalating into significant problems that compromise system efficiency.
Key Maintenance Practices
To maintain optimal performance, several key maintenance practices should be followed:
Routine Inspections: Conducting regular inspections helps identify wear and tear on components such as belts and bearings. This proactive approach allows for early detection of potential issues.
Cleaning: Regular cleaning of ventilation systems is essential to prevent dust accumulation, which can impede airflow and increase energy consumption.
Component Replacement: Prompt replacement of worn or damaged parts is vital for maintaining system efficiency and reliability.
Environmental Compliance: Adhering to environmental and safety standards not only enhances reliability but also ensures safe operation in various settings.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Radial fans may encounter several operational problems, and addressing these through systematic troubleshooting is important:
Noise Problems
Unusual noises can indicate mechanical issues, such as misalignment or loose components. Regular inspections to secure bolts and components can help mitigate these concerns. Experts emphasize the importance of routine checks to identify noise sources early, as they often signal underlying issues that may lead to operational failures if neglected.
Overheating
Overheating may result from inadequate ventilation or excessive load on the fan motor. Ensuring that the motor is not overloaded and confirming proper airflow around it can significantly enhance its longevity. Monitoring temperature levels and implementing preventive measures are recommended to avoid overheating problems.
Vibration Issues
Excessive vibration is a common indicator of misalignment, imbalance, or worn bearings. Regular inspections are imperative to prevent damage, and monitoring vibration levels can help avert substantial operational failures. Upon detecting imbalance, it is advisable to review the maintenance logs and evaluate the fan’s dynamic conditions.
Insufficient Airflow
If a fan fails to deliver the expected airflow, it is important to investigate potential blockages in ductwork, verify the fan’s operational speed, and ensure it is properly sized for its application. A comprehensive analysis of the entire system, including duct design and fan placement, is often necessary to rectify airflow deficiencies. By prioritizing routine maintenance and employing effective troubleshooting techniques, users can enhance the performance and lifespan of radial fans, ensuring they operate efficiently in various applications.
Environmental Impact
Radial fans play a significant role in promoting environmental sustainability through various mechanisms. By reducing energy consumption and lowering greenhouse gas emissions, these fans contribute positively to environmental conservation efforts. The operational efficiency of radial fans not only enhances productivity in industrial applications but also minimizes the need for additional fuel, thus reducing operational expenses and environmental footprints.
Energy Efficiency and Greenhouse Gas Emissions
The implementation of Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) in conjunction with radial fans can lead to substantial energy savings. VFDs allow for precise control of fan speed, thereby reducing energy consumption compared to traditional on-off motor operations. This reduction in energy use directly correlates with decreased greenhouse gas emissions associated with energy production, making VFDs an effective tool for industries aiming to lower their environmental impact.
Durability and Lifecycle Management
High-quality radial fans are designed for durability, often constructed from corrosion-resistant materials that extend their service life. A longer lifecycle not only reduces the frequency of replacements but also minimizes industrial waste and conserves resources. Sustainable practices are further promoted as companies can focus on maintenance rather than disposal, thereby lessening the environmental implications of manufacturing and waste.
Indoor Air Quality and Worker Safety
Radial fans also contribute to social sustainability by improving indoor air quality in various settings, including industrial facilities and workshops. By ensuring adequate ventilation and effective pollutant removal, these fans support better health and safety standards for workers. Good indoor air quality is crucial not only for employee comfort but also for enhancing productivity and overall workplace morale.
Compliance with Environmental Standards
The selection of radial fans that comply with environmental and safety regulations—such as RoHS and EMC—ensures that these devices operate reliably while contributing to a safer and more eco-friendly environment. The implementation of noise reduction strategies is also essential in sensitive environments to mitigate the acoustic impact of fan installations. Compliance with noise regulations can improve both the safety and comfort of workers, emphasizing the importance of selecting appropriate fan types for specific applications.
Future Trends
The future of radial fans is poised for significant advancements driven by technological innovation and evolving market demands. Key trends shaping the landscape include enhanced energy efficiency, the integration of smart technologies, and an increasing focus on sustainability.
Energy Efficiency and Performance Optimization
As energy costs continue to rise and sustainability becomes a critical concern, manufacturers are focusing on maximizing energy efficiency in radial fans. This includes the development of high-efficiency electronically commutated (EC) motors that can achieve energy savings of up to 70% compared to traditional AC motors. Additionally, advancements in fan design are aimed at optimizing airflow while minimizing noise levels and enhancing performance across various applications, such as HVAC and industrial ventilation systems.
Adoption of Smart Technologies
The incorporation of smart technologies into radial fans is set to transform their operational capabilities. Features such as real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and automation will allow for greater control and efficiency. Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) are a prime example, enabling fans to adjust their speed and torque based on load requirements, leading to significant energy savings and extended equipment lifespan. This trend towards smarter systems aligns with broader Industry 4.0 initiatives, where data-driven insights are leveraged to optimize performance.
Sustainability Initiatives
In light of global sustainability goals, the demand for eco-friendly solutions in fan technology is expected to increase. Radial fans will likely see more stringent regulatory standards aimed at reducing energy consumption and carbon footprints. Companies that adopt innovative approaches, such as using sustainable materials in manufacturing and developing energy-efficient designs, will be well-positioned in the market. Moreover, the agricultural sector is increasingly recognizing the role of VFDs in enhancing operational efficiency and resource management, further underscoring the importance of sustainability.
Customization and Market Competition
As the market for radial fans becomes more competitive, there is a growing demand for customization to meet specific application needs. Companies are responding by offering a wider range of options, from basic models to advanced units with integrated communication capabilities. This trend is particularly evident in sectors such as medical and telecommunication, where tailored solutions are critical for performance and compliance.